रासायनिक अभिक्रिया क्या है?रासायनिक अभिक्रिया क्या है,एवं कब और क्यों होती हैं?रसायनिक समीकरण।कंकाली रसायनिक समीकरण
Such reactions in which there is a change in the organization, properties and structure of substances, are called reactions. These reactions are of two types-
1. Nuclear Reaction
2. Chemical Reaction
Nuclei of the atom take part in nuclear reactions, in these reactions the nature of the atoms changes, that is, one type of atom gets converted into another type of atom. In a chemical reaction, electrons take part after the atoms, thus in a chemical reaction, atoms participate almost inseparably and their individual form is never destroyed.
Molecules of different substances participating in a chemical reaction first split into atoms or different groups of atoms.After these processes, there is a rearrangement of atoms or groups of atoms and new molecules are formed, in this way some old bonds formed between atoms in a chemical reaction are broken and some new bonds are formed and one type of molecule is of another type.
In a chemical reaction, there is a change in the organization and structure of the particles of matter, due to which the properties of the substances also change.
For example, water is formed by the combination of oxygen and hydrogen. Water is a compound and its properties are completely different from those of hydrogen and oxygen.
Water (H2O) is generally used for drinking. It is dihydrogen monoxide containing two moles of hydrogen and one mole of oxygen. This standard is found in the liquid state at room temperature.h2O, a clear, colourless, odourless, tasteless liquid that freezes into ice below 0 °C and boils above 100 °C.
Density: 997 kg/m³
Formula: H₂O
Molar mass: 18.01528 g/mol
Boiling point: 100 °C
Melting point: 0 °C
Triple point temperature: 0.01 °C
IUPAC ID: Oxidane, Water
रासायनिक अभिक्रिया क्या है?
ऐसी क्रियाएं जिनमें पदार्थों के संगठन, गुणों तथा संरचना में परिवर्तन होता है, इन्हें अभिक्रिया का जाता है। बी अभिक्रियाएं दो प्रकार की होती हैं-
- नाभिकीय अभिक्रिया
- रसायनिक अभिक्रिया
नाभिकीय अभिक्रिया में परमाणु के नाभिक भाग लेते हैं इन अभिक्रिया में परमाणुओं का स्वरूप परिवर्तित हो जाता है अर्थात एक प्रकार के परमाणु दूसरे प्रकार के परमाणु में परिवर्तित हो जाते हैं। रासायनिक अभिक्रिया में परमाणुओं के बाद में इलेक्ट्रॉन भाग लेते हैं इस प्रकार रासायनिक अभिक्रिया में परमाणु लगभग अविभाज्य रूप से भाग लेते हैं तथा उनका निजी स्वरूप कभी भी नष्ट नहीं होता है।
रासायनिक प्रतिक्रिया में भाग लेने वाले विभिन्न पदार्थों के अणु पहले परमाणुओं या परमाणुओं के विभिन्न समूहों में विभाजित होते हैं।इन प्रक्रियाओं के पश्चात परमाणु अथवा परमाणुओं के समूह की रिअरेंजमेंट होती है तथा नए अणु बनकर आते हैं इस प्रकार रसायनिक अभिक्रिया में परमाणुओं के मध्य बनने वाले कुछ पुराने बन्ध टूट जाते हैं और कुछ बंध नए बन जाते हैं तथा एक प्रकार के अणु दूसरे प्रकार के अणु में परिवर्तित हो जाते हैं इस प्रकार रसायनिक अभिक्रिया में पदार्थ के कणों के संगठन तथा संरचना में परिवर्तन होता है जिसके कारण पदार्थों के गुण भी परिवर्तित हो जाते हैं।
उदाहरण के लिए, पानी ऑक्सीजन और हाइड्रोजन के संयोजन से बनता है। पानी एक यौगिक है और इसके गुण हाइड्रोजन और ऑक्सीजन से बिल्कुल अलग हैं।
पानी–
पानी (H2O) आमतौर पर पीने के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है। यह डाइहाइड्रोजन मोनोऑक्साइड है जिसमें दो मोल हाइड्रोजन और एक मोल ऑक्सीजन होता है। यह मानक कमरे के तापमान पर तरल अवस्था में पाया जाता है।
h2O, एक स्पष्ट, रंगहीन, गंधहीन, स्वादहीन तरल है जो 0 डिग्री सेंटीग्रेड से नीचे बर्फ में जम जाता है और 100 डिग्री सेंटीग्रेड से ऊपर उबलता है।
Density: 997 kg/m³
Formula: H₂O
Molar mass: 18.01528 g/mol
Boiling point: 100 °C
Melting point: 0 °C
Triple point temperature: 0.01 °C
IUPAC ID: Oxidane, Water
और अधिक पढ़ें- यहाँ click करें
रासायनिक अभिक्रिया क्या है कब और क्यों होती हैं?
Friends, as we all know that physical and chemical changes keep taking place along with energy changes. If the energy of a system is more, then it is less stable and if the energy of the system is less then it is more stable. If a toy is released from the hand, it falls down, this is because the toy has more potential energy in the hand and it is less temporary.
Remaining temporary, all the objects of the world tend to attain permanence. So the toy tries to fall down. Similarly, when two or more substances are brought under the influence of temperature, pressure or other factors, they try to convert into some other substance to achieve stability. Due to which more stable substances are formed, then chemical reactions start to take place. If more stable substances are not obtained, then the chemical reaction cannot take place.
In any chemical reaction, the free energy of the reactants is greater than the free energy of the products and the free energy change is always negative.
घरों में पढ़ाने हेतु अध्यापक बुलाने के लिए अथवा online tutor hire करने के लिए अभी संपर्क करें-9792206168
अथवा विजिट करें- www.gsptutorial.com
दोस्तों जैसा कि हम सभी जानते हैं भौतिक तथा रासायनिक परिवर्तन ऊर्जा परिवर्तन के साथ संपन्न होते रहते हैं.यदि किसी निकाय की उर्जा अधिक है, तो वह कम स्थाई होता है तथा यदि निकाय की उर्जा कम है तो वह अधिक स्थाई होता है.जैसे की यदि एक खिलौने को हाथ से छोड़ा जाता है तो वह नीचे गिर जाता है इसका कारण यह है कि हाथ में खिलौने की स्थितिज ऊर्जा ज्यादा रहती है तथा वह कम अस्थाई होता है जमीन पर खिलौने की स्थितिज ऊर्जा कम है इसके साथ-साथ वह वहां ज्यादा अस्थाई रहता है दुनिया के सभी पदार्थ स्थायित्व को प्राप्त करने की प्रवृत्ति रखते हैं।
अतः खिलौना नीचे गिरने का प्रयास करता है. इसी प्रकार जब दो या दो से अधिक पदार्थों को ताप दाब या अन्य कारकों के प्रभाव में लाया जाता है तो वह स्थायित्व प्राप्त करने हेतु कुछ अन्य पदार्थों में परिवर्तित होने का प्रयास करते हैं. जिससे अधिक स्थायित्व वाले पदार्थों का निर्माण होता है, तो रसायनिक अभिक्रिया संपन्न होने लगती है. यदि अधिक स्थायित्व वाले पदार्थ प्राप्त नहीं होते हैं तो रासायनिक अभिक्रिया संपन्न नहीं हो पाती है. किसी भी रसायनिक अभिक्रिया में अभिकारकों की मुक्त ऊर्जा उत्पादो की मुक्त ऊर्जा से अधिक होती है और मुक्त ऊर्जा परिवर्तन का मन हमेशा ऋण आत्मक होता है.
रसायनिक समीकरण-
Chemical Equation-
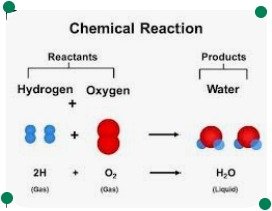
Hydrogen and oxygen react with each other to form water and some amount of energy, if it is written in words, it becomes very long, it can also be written in short form. This short form of the reaction is called the word equation.
2H2 + O2 = 2H2O + Energy
Hydrogen and oxygen are substances in which chemical changes take place, they are called reactants.In this reaction a new substance is formed which is called a product.The change in reaction is shown by an arrow. The reactants are written on the left side of the arrow by putting a sign (+) in the middle. And they are written on the right side of the arrow by putting a sign (+) in the middle of the product. The arrowhead indicates the direction of the reaction, it is always towards the product.
हाइड्रोजन और ऑक्सीजन आपस में क्रिया करके पानी और कुछ मात्रा में ऊर्जा बनाते हैं, अगर इसे शब्दों में लिखा जाए तो यह बहुत लंबा हो जाता है, इसे संक्षिप्त रूप में भी लिखा जा सकता है। प्रतिक्रिया के इस संक्षिप्त रूप को शब्द समीकरण कहा जाता है। हाइड्रोजन और ऑक्सीजन ऐसे पदार्थ हैं जिनमें रासायनिक परिवर्तन होते हैं, वे अभिकारक कहलाते हैं। इस रासायनिक अभिक्रिया में एक नया पदार्थ बनता है जिसे उत्पाद कहते हैं।
2H2 + O2 = 2H2O + Energy
एक तीर के द्वारा के अभिक्रिया में परिवर्तन को दिखाया गया है अभिकारको के बीच में योग (+) का चिन्ह लगाकर उन्हें तीर के बाई तरफ लिखा जाता है, तथा उत्पाद के बीच में भी योग (+) का चिन्ह लगाकर उन्हें तीर के दाएं तरफ लिखा जाता है.तीर का सिरा रासायनिक अभिक्रिया होने की दिशा को बताता है यह हमेशा उत्पाद की ओर ही रहता है।
घरोंमें पढाने हेतु Tutor के लिए संपर्क करें-Visit Here
Writing a Chemical Equation Using a Chemical Formula-
रासायनिक सूत्र का उपयोग करके रासायनिक समीकरण लिखना-
Using chemical formulas instead of words to write chemical equations makes chemical equations more concise and useful. The chemical equation can be written by means of formulas as follows-
2H2 + O2 = 2H2O + Energy
रासायनिक समीकरण लिखने के लिए शब्दों के बजाय रासायनिक सूत्रों का उपयोग करना रासायनिक समीकरणों को अधिक संक्षिप्त और उपयोगी बनाता है। रासायनिक समीकरण को सूत्र द्वारा निम्न प्रकार से लिखा जा सकता है-
2H2 + O2 = 2H2O + Energy
Balanced Chemical Equation
संतुलित रासायनिक समीकरण
If the number of atoms of the elements on either side of the arrow mark is compared in the above-written equation, then the number of atoms of each element is same on either side of the arrow mark, so it will be said that the chemical equation is in a balanced state. Mass is neither created nor destroyed in any chemical reaction, or the total mass of the product elements in any chemical reaction is equal to the total mass of the reactant elements.
ऊपर लिखे गए समीकरण में तीर के निशान के दोनों ओर के तत्वों के परमाणु की संख्या की तुलना किया जाए ,तो तीर के निशान के दोनों ओर प्रत्येक तत्व के परमाणुओं की संख्या समान है इसलिए यह कहा जाएगा कि रसायनिक समीकरण संतुलित अवस्था में है. किसी भी रासायनिक अभिक्रिया में द्रव्यमान का ना तो नव निर्माण होता है और ना ही विनाश होता है, अथवा किसी भी रसायनिक अभिक्रिया में उत्पाद तत्वों का कुल द्रव्यमान अभिकारक तत्वों के कुल द्रव्यमान के बराबर ही होता है
Skeletal Chemical Equation-
कंकाली रसायनिक समीकरण-
When the mass of both the right side of the arrow and the left side of the arrow of a chemical equation is not equal, then such a chemical equation is called skeletal chemical equation, this reaction is not balanced.
Ex- Mg+O2=MgO
As can be seen in the above equation, the number of atoms of elements is not the same on both sides. The oxygen atom to the left of the equal sign is numbered 2 while the number to the right is 1.
*When lead nitrate is heated, the lighter oxides form nitrogen oxides and oxygen.
जब किसी रासायनिक समीकरण के दोनों और तीर के दाएं तथा तीर के बाएं तरफ का द्रव्यमान बराबर नहीं होता है तो ऐसी रसायनिक समीकरण को कंकाली रसायनिक समीकरण कहते हैं यह अभिक्रिया संतुलित नहीं रहती है।
Ex- Mg+O2=MgO
*जैसा कि उपरोक्त समीकरण में देखा जा सकता है, तत्वों के परमाणुओं की संख्या दोनों तरफ समान नहीं होती है। समान चिह्न के बाईं ओर ऑक्सीजन परमाणु की संख्या 2 है जबकि दाईं ओर की संख्या 1 है।
*लेड नाइट्रेट को गर्म करने पर हल्के ऑक्साइड नाइट्रोजन ऑक्साइड और ऑक्सीजन बनाते हैं।
रसायनिक अभिक्रिया के प्रकार (Types Of Chemical Reactions)
Many chemical reactions are found in the world. Many similarities are also found in these chemical reactions. If there is a special similarity in a reaction, then on the basis of that similarity, this reaction will be called a similar type of reaction. Similarly, if there is any other kind of similarity in a reaction, then on the basis of similarity these reactions are given another special name. And this reaction is a special type of reaction. Therefore, chemical reactions are of different types on the basis of similarity. The main types of chemical reactions are described below.
संसार में अनेक रासायनिक अभिक्रियाएँ पाई जाती हैं। इन रासायनिक अभिक्रियाओं में भी कई समानताएँ पाई जाती हैं। यदि किसी अभिक्रिया में विशेष समानता हो तो उस समानता के आधार पर यह अभिक्रिया उसी प्रकार की अभिक्रिया कहलाएगी। इसी प्रकार यदि किसी अभिक्रिया में किसी अन्य प्रकार की समानता हो तो समानता के आधार पर इन अभिक्रियाओं को एक और विशेष नाम दिया जाता है। और यह अभिक्रिया एक विशेष प्रकार की अभिक्रिया है। अतः समानता के आधार पर रासायनिक अभिक्रियाएँ विभिन्न प्रकार की होती हैं। रासायनिक प्रतिक्रियाओं के मुख्य प्रकार नीचे वर्णित हैं।
- Addition Reaction-योगात्मक अभिक्रिया
- Substitution Reaction- प्रतिस्थापन अभिक्रिया
- Irreversible Reaction-अनुत्क्रमणीय अभिक्रिया
- Reversible Reaction-उत्क्रमणीय अभिक्रिया
- decomposition reaction-अपघटन अभिक्रिया
- decomposition reaction-वियोजन अभिक्रिया
- amphibolic decomposition reaction-उभय अपघटन अभिक्रिया
- exothermic reaction-ऊष्माक्षेपी अभिक्रिया
- endothermic reaction-ऊष्माशोषी अभिक्रिया
- reduction reaction-अपचयन अभिक्रिया
Addition Reaction(योगात्मक अभिक्रिया)-
The reactions in which two or more substances combine to form only one substance are called additive reactions.
As a result of the additive reaction of carbon monoxide and chlorine, the poisonous gas ‘phosgene’ is formed, which is also known as carbonyl chloride.
CO + Cl2= COCl2
वे अभिक्रियाएं जिनमें दो या दो से अधिक पदार्थों के सहयोग से केवल एक पदार्थ बनाते हैं योगात्मक अभिक्रियायें कहलाती हैं।
कार्बन मोनो ऑक्साइड तथा क्लोरीन की योगात्मक अभिक्रिया के फल स्वरुप विषैली गैस ‘फास्जीन’ का निर्माण होता है जिसे कार्बोनेल क्लोराइड भी कहा जाता है।
CO + Cl2= COCl2
Substitution Reaction- प्रतिस्थापन अभिक्रिया-
Substitution reactions are those reactions in which one atom or group of atoms of a compound is replaced by another atom or group of atoms, this type of reaction is called substitution reaction.
The reaction between methane and chlorine in the presence of sunlight is as follows-
CH4 (methane) + Cl2 (chlorine) = CH3Cl (methyl chloride) + HCl (hydrogen chloride gas)
प्रतिस्थापन अभिक्रियाएँ वे अभिक्रियाएँ होती हैं जिनमें किसी यौगिक के एक परमाणु या परमाणुओं के समूह को दूसरे परमाणु या परमाणुओं के समूह द्वारा प्रतिस्थापित किया जाता है, इस प्रकार की अभिक्रिया प्रतिस्थापन अभिक्रिया कहलाती है।
सूर्य के प्रकाश की उपस्थिति में Methane और क्लोरीन के बीच की अभिक्रिया कुछ इस प्रकार से होती है-
CH4 (मिथेन) + Cl2(क्लोरीन) = CH3Cl (मैथिल क्लोराइड) + HCl (हाइड्रोजन क्लोराइड गैस)
अनुत्क्रमणीय अभिक्रिया(Irreversible reaction)-
A reaction that takes place in only one direction is called an irreversible reaction. In these reactions the reactants are almost completely converted into products, the products of these reactions cannot be recovered by mixing in any proportion or under any conditions.
2Na + 2H2O = 2NaOH + H2 (Gas)
केवल एक ही दिशा में होने वाली अभिक्रिया अपरिवर्तनीय अभिक्रिया कहलाती है। इन प्रतिक्रियाओं में अभिकारक लगभग पूरी तरह से उत्पादों में परिवर्तित हो जाते हैं, इन प्रतिक्रियाओं के उत्पादों को किसी भी अनुपात में या किसी भी स्थिति में मिलाकर पुनर्प्राप्त नहीं किया जा सकता है।
2Na + 2H2O = 2NaOH + H2 (गैस)
उत्क्रमणीय अभिक्रिया(Reversible reaction)-
Reversible reactions are those reactions which can occur in both the directions under the same conditions are called reversible reactions. This reaction takes place in the normal state, the product in the first reaction, while the reactant in the second reaction. The product in the second reaction is the same as the reactant in the first reaction. Therefore, this reaction can proceed in both forward and backward directions. In chemical equations for a reversible reaction, reversibility sign is used in place of arrow or equal. The reaction which appears on the left and right sides of these equations is called forward reaction. And the reaction which is shown from right to left side is called reverse reaction.
प्रतिवर्ती अभिक्रियाएँ वे अभिक्रियाएँ होती हैं जो समान परिस्थितियों में दोनों दिशाओं में हो सकती हैं, उत्क्रमणीय अभिक्रियाएँ कहलाती हैं। यह अभिक्रिया सामान्य अवस्था में होती है, पहली अभिक्रिया में उत्पाद होता है, जबकि दूसरी प्रतिक्रिया में अभिकारक होता है। दूसरी अभिक्रिया में उत्पाद वही है जो पहली अभिक्रिया में अभिकारक है। इसलिए, यह अभिक्रिया आगे और पीछे दोनों दिशाओं में आगे बढ़ सकती है। उत्क्रमणीय अभिक्रिया के रासायनिक समीकरणों में तीर या बराबर के स्थान पर उत्क्रमणीयता चिन्ह का प्रयोग किया जाता है। वह अभिक्रिया जो इन समीकरणों के बाएँ और दाएँ पक्ष में दिखाई देती है, अग्र अभिक्रिया कहलाती है। और वह अभिक्रिया जो दायीं ओर से बायीं ओर दिखाई जाती है, विपरीत अभिक्रिया कहलाती है।
घरों में पढ़ाने हेतु अध्यापक बुलाने के लिए अथवा online tutor hire करने के लिए अभी संपर्क करें-9792206168
अथवा विजिट करें- www.gsptutorial.com
अपघटन अभिक्रिया(Decomposition Reaction)
The reversible reactions in which the molecules of a substance split into two or more simpler molecules are called decomposition reactions. This reaction takes place under the influence of heat and electricity. The decomposition under the influence of heat is called thermal decomposition reaction and the decomposition under the influence of electricity is called electrolysis reaction.
वे उत्क्रमणीय अभिक्रियाएँ जिनमें किसी पदार्थ के अणु दो या दो से अधिक सरल अणुओं में विभाजित हो जाते हैं, अपघटन अभिक्रियाएँ कहलाती हैं। यह प्रतिक्रिया गर्मी और बिजली के प्रभाव में होती है। गर्मी के प्रभाव में अपघटन को थर्मल अपघटन अभिक्रिया कहा जाता है और बिजली के प्रभाव में अपघटन को इलेक्ट्रोलिसिस अभिक्रिया कहा जाता है।
वियोजन अभिक्रिया (Dissociation reaction)-
Those reversible reactions in which the molecules of a substance split into two or more simpler molecules are called dissociation.
Decomposition and decomposition reactions are almost the same, the only difference is that decomposition reactions are irreversible while decomposition reactions are reversible.
वे उत्क्रमणीय अभिक्रियाएं जिनमें किसी पदार्थ के अणु दो या दो से अधिक सरल अणुओं में विभाजित हो जाते हैं, वियोजन कहलाते हैं।
अपघटन और अपघटन प्रतिक्रियाएं लगभग समान होती हैं, केवल अंतर यह है कि अपघटन अभिक्रियाएं अपरिवर्तनीय होती हैं जबकि अपघटन अभिक्रियाएं प्रतिवर्ती होती हैं।
The rest of the information of this chapter is given in the next part, the link of which is given below, you can get more information by going to the next article by clicking below.
इस अध्याय की बाकी जानकारी अगले भाग में दी गई है जिसका लिंक नीचे दिया गया है, अधिक जानकारी आप अगले लेख में नीचे क्लिक करके प्राप्त कर सकते हैं।
